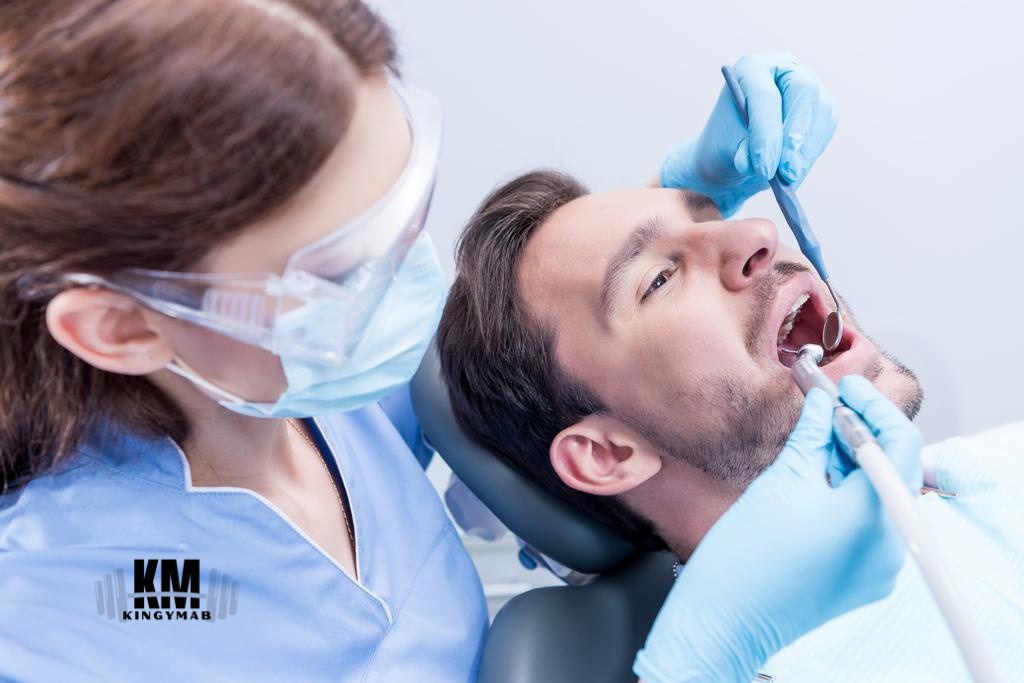
Introduction
Gum recession is a common dental issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth starts to pull away, exposing more of the tooth’s surface and root. This can lead to various problems, including tooth sensitivity, increased risk of decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatments available for receding gums, with a particular focus on how I successfully healed my receding gums.
Understanding Receding Gums
What Are Receding Gums?
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is a condition where the gum tissue gradually pulls away from the teeth, exposing the root surface. This can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Poor oral hygiene and plaque buildup
- Aggressive brushing or flossing
- Periodontal disease (gum disease)
- Genetics (thin or receding gum tissue)
- Hormonal changes
- Orthodontic treatment (braces or other dental appliances)
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
Symptoms of Receding Gums
The signs and symptoms of receding gums can vary from person to person, but some common indicators include:
- Exposed tooth roots
- Tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet substances
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Longer-looking teeth
- Gaps between teeth and gums
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek professional dental care to prevent further gum recession and potential complications.
Causes of Receding Gums
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of receding gums. Understanding these causes is crucial in preventing and treating the condition.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which can irritate and inflame the gum tissue, causing it to recede over time.
Aggressive Brushing or Flossing
While proper oral hygiene is essential, brushing or flossing too vigorously can damage the delicate gum tissue, leading to recession.
Periodontal Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and the supporting structures of the teeth. If left untreated, it can cause significant gum recession and even tooth loss.
Genetics
Some people are genetically predisposed to having thin or receding gum tissue, making them more susceptible to gum recession.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can increase the risk of gum recession, as these changes can affect the body’s inflammatory response.
Orthodontic Treatment
Certain orthodontic treatments, such as braces or other dental appliances, can put pressure on the gums and contribute to recession if not properly monitored and adjusted.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and other forms of tobacco use can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections, increasing the risk of gum disease and subsequent gum recession.
My Experience with Receding Gums

The Early Signs
Like many others, I didn’t notice the early signs of gum recession until it became more apparent. It started with occasional tooth sensitivity and slight bleeding when I brushed my teeth. At first, I brushed it off as nothing serious, but as time went on, the symptoms became more pronounced.
The Realization
It wasn’t until my regular dental check-up that I realized the severity of the issue. My dentist pointed out the exposed tooth roots and the gaps between my teeth and gums, indicating advanced gum recession. I was shocked and concerned, as I had always been diligent about my oral hygiene routine.
The Contributing Factors
After a thorough examination and discussion with my dentist, we identified a few potential contributing factors:
- Genetics: My family has a history of thin gum tissue, which made me more susceptible to gum recession.
- Aggressive Brushing: While I was meticulous about brushing, I realized that my technique was too aggressive, causing trauma to my gum tissue over time.
- Orthodontic Treatment: I had braces during my teenage years, which may have contributed to the gum recession due to the pressure and irritation caused by the appliances.
The Turning Point
Determined to address the issue before it progressed further, I committed to a comprehensive treatment plan recommended by my dentist. This plan included a combination of professional dental treatments and lifestyle changes, which I’ll discuss in detail in the following sections.
Professional Dental Treatments
Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
The first step in my treatment plan was a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing. This involved the removal of plaque, tartar, and bacterial toxins from the tooth surfaces and root areas below the gum line. This process helps reduce inflammation and create a clean environment for the gums to heal and reattach to the teeth.
Gum Graft Surgery
In areas where the gum recession was severe, my dentist recommended a gum graft surgery. During this procedure, a small amount of gum tissue was taken from the roof of my mouth (or sometimes from a donor source) and transplanted to the receded areas. This helped cover the exposed tooth roots and prevent further recession.
Dental Bonding
For some areas where the recession was not severe enough to warrant a graft, my dentist performed dental bonding. This involved applying a tooth-colored resin material to cover the exposed root surfaces, protecting them from sensitivity and potential decay.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Care
While professional dental treatments were essential, I also had to make significant lifestyle changes and improve my home care routine to ensure long-term success.
Proper Brushing Technique
One of the most crucial changes I made was adjusting my brushing technique. I learned the proper way to brush, using gentle, circular motions and applying minimal pressure. This helped prevent further trauma to my gum tissue and allowed it to heal properly.
Flossing Regularly
I also became more diligent about flossing regularly. Flossing helps remove plaque and debris from areas that a toothbrush cannot reach, reducing the risk of gum inflammation and recession.
Using Desensitizing Toothpaste
To alleviate the tooth sensitivity caused by exposed root surfaces, I started using a desensitizing toothpaste containing compounds that help block the transmission of pain signals from the teeth.
Quitting Smoking
While I wasn’t a heavy smoker, I did indulge occasionally. However, after learning about the detrimental effects of smoking on gum health, I made the decision to quit entirely. This not only improved my overall oral health but also reduced the risk of further gum recession.
Stress Management
Stress can have a negative impact on our bodies, including our oral health. To promote healing and prevent further gum recession, I incorporated stress management techniques into my daily routine, such as meditation, yoga, and regular exercise.
The Results and Ongoing Maintenance
Gradual Improvement
The journey to healing my receding gums was not an overnight process, but with consistent effort and dedication, I began to see gradual improvements. The gum tissue started to reattach to the teeth, and the sensitivity subsided over time.
Routine Dental Check-ups
To maintain the progress and ensure the long-term health of my gums, I continued to visit my dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings. This allowed my dentist to monitor the condition of my gums and address any potential issues early on.
Ongoing Home Care
I also remained diligent in my home care routine, brushing and flossing correctly, using desensitizing toothpaste, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This ongoing commitment has been crucial in preventing further gum recession and maintaining the positive results I’ve achieved.
Tips for Preventing and Managing Receding Gums
Based on my personal experience and guidance from dental professionals, here are some valuable tips for preventing and managing receding gums:
Practice Proper Oral Hygiene
Brushing and flossing correctly is the foundation for maintaining healthy gums. Make sure to brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using gentle circular motions. Floss once daily to remove plaque and debris from hard-to-reach areas.
Avoid Aggressive Brushing and Flossing
While it’s important to be thorough in your oral hygiene routine, avoid being too aggressive. Brushing or flossing too vigorously can damage the delicate gum tissue and contribute to recession.
Quit Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use can significantly increase the risk of gum disease and recession. Quitting these habits can improve your overall oral health and reduce the likelihood of gum issues.
Manage Stress Levels
Stress can have a negative impact on your body’s ability to fight off infections and heal properly. Incorporate stress management techniques into your routine, such as meditation, yoga, or regular exercise.
Seek Professional Dental Care
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for detecting and addressing any potential gum issues early on. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice and treatment if you notice signs of gum recession or other oral health concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can receding gums grow back?
Unfortunately, receding gums cannot grow back on their own. However, with proper treatment and care, it is possible to prevent further recession and improve the appearance and health of the affected areas.
How long does it take to heal receding gums?
The healing process for receding gums can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the treatment methods used. In general, it can take several weeks to several months to see significant improvement. Consistency and patience are key during the healing process.
Can receding gums lead to tooth loss?
Yes, if left untreated, severe gum recession can lead to tooth loss. As the gum tissue recedes, it exposes more of the tooth’s root surface, making it susceptible to decay and potential loss if the issue progresses.
Can braces cause receding gums?
While braces themselves do not directly cause gum recession, improper oral hygiene during orthodontic treatment can contribute to the development of gum issues, including recession. It’s crucial to maintain excellent oral hygiene and attend regular dental check-ups while wearing braces.
Can receding gums be prevented?
While some factors contributing to gum recession, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, there are several steps you can take to prevent or minimize the risk of receding gums. These include practicing proper oral hygiene, avoiding aggressive brushing and flossing, quitting smoking, and managing stress levels.
Statistics and Facts
| Statistic | Value |
| Percentage of adults aged 30 and older with gum recession | Over 50% |
| Prevalence of gum recession in smokers compared to non-smokers | Up to 3 times higher |
| Likelihood of developing gum recession after orthodontic treatment | Increased risk |
| Percentage of people with untreated gum disease who develop gum recession | Over 70% |
| Success rate of gum graft surgeries in treating gum recession | Approximately 90% |
Real-Life Success Stories
Sarah’s Journey
“I was devastated when my dentist told me about my receding gums. I had always been diligent about brushing and flossing, but I learned that my aggressive technique was causing more harm than good. After undergoing a deep cleaning and gum graft surgery, along with adjusting my brushing habits, I’ve seen a remarkable improvement. My gums are healthier, and I’m no longer experiencing sensitivity.”
Michael’s Experience
“As a former smoker, I didn’t realize the impact it was having on my oral health until I started noticing my gums receding. It was a wake-up call for me to quit smoking and take better care of my teeth and gums. With the help of my dentist and a commitment to a improved oral hygiene routine, I’ve been able to reverse the recession and keep my gums in great shape.”
Emily’s Transformation
“Gum recession ran in my family, so I knew I was at a higher risk. When I started noticing the early signs, I didn’t hesitate to seek professional help. My dentist recommended a combination of scaling, root planing, and dental bonding to cover the exposed root surfaces. The results have been amazing, and I feel more confident about my smile.”
The Importance of Early Intervention
One of the key takeaways from my experience is the importance of early intervention when it comes to receding gums. The earlier you address the issue, the better your chances of preventing further recession and maintaining good oral health.
| Gum Recession Stage | Treatment Options | Potential Complications |
| Early | Professional cleaning, improved oral hygiene, desensitizing toothpaste | Tooth sensitivity, increased risk of decay |
| Moderate | Deep cleaning, gum grafting, dental bonding | Exposed root surfaces, bone loss |
| Advanced | Extensive gum surgery, tooth extraction | Tooth loss, periodontal disease |
As the table illustrates, the earlier you seek treatment for receding gums, the less invasive and more effective the treatment options are. By catching the issue early, you can often reverse or halt the progression of gum recession with professional cleanings, improved oral hygiene, and desensitizing toothpaste.
However, if the condition progresses to moderate or advanced stages, more extensive treatments like gum grafting, dental bonding, or even tooth extraction may be required. These procedures are typically more expensive, time-consuming, and carry a higher risk of complications.
The Role of Genetics and Other Contributing Factors
While my experience highlights the importance of proper oral hygiene and lifestyle factors, it’s also essential to acknowledge the role of genetics and other contributing factors in the development of receding gums.
Genetics and Gum Recession
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to having thin or fragile gum tissue, which can increase their risk of gum recession. In these cases, even with excellent oral hygiene practices, individuals may be more susceptible to gum issues.
| Genetic Factor | Impact |
| Thin or fragile gum tissue | Increased susceptibility to gum recession, even with good oral hygiene |
| Family history of gum disease | Higher risk of developing gum issues, including recession |
| Abnormal tooth positioning or alignment | Can create areas prone to plaque buildup and gum inflammation |
| Weakened immune response | Reduced ability to fight off infections that can lead to gum disease and recession |
| Hormonal imbalances | Can increase inflammation and affect the body’s response to plaque and bacteria |
As you can see, genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s risk for gum recession. However, it’s important to note that even with a genetic predisposition, maintaining good oral hygiene practices and addressing any underlying issues can help minimize the risk and prevent further progression of the condition.
Other Contributing Factors
In addition to genetics, there are several other factors that can contribute to the development of receding gums, including:
| Genetic Factor | Impact |
| Thin or fragile gum tissue | Increased susceptibility to gum recession, even with good oral hygiene |
| Family history of gum disease | Higher risk of developing gum issues, including recession |
| Abnormal tooth positioning or alignment | Can create areas prone to plaque buildup and gum inflammation |
| Weakened immune response | Reduced ability to fight off infections that can lead to gum disease and recession |
| Hormonal imbalances | Can increase inflammation and affect the body’s response to plaque and bacteria |
While some of these factors may be beyond our control, being aware of them and taking proactive measures can help mitigate their impact on gum health. Regular dental check-ups, maintaining a balanced diet, and addressing any underlying health conditions can all contribute to better overall oral health and reduce the risk of gum recession.
The Emotional and Social Impact of Receding Gums
Beyond the physical implications, receding gums can also have a significant emotional and social impact on an individual’s life. It’s important to acknowledge and address these aspects as part of the overall journey to healing and recovery.
Self-Confidence and Self-Esteem
The appearance of receding gums and exposed tooth roots can be a source of self-consciousness and insecurity for many individuals. This can potentially lead to a lack of confidence in social situations, affecting personal and professional relationships.
Emotional Well-being
The stress and anxiety associated with dental issues like receding gums can take a toll on an individual’s emotional well-being. It’s important to prioritize self-care and seek support from loved ones or mental health professionals if needed.
Social Interactions
Tooth sensitivity and discomfort caused by receding gums can make individuals hesitant to engage in certain social activities, such as dining out or engaging in conversations. This can lead to feelings of isolation and a diminished quality of life.
Professional Implications
In some cases, severe gum recession can impact an individual’s ability to perform certain professional duties, particularly those that require public speaking or client-facing interactions. This can potentially affect career advancement and job satisfaction.
By addressing the physical aspects of receding gums through proper treatment and care, individuals can also alleviate the emotional and social burdens associated with the condition. Seeking support from loved ones, counseling services, or support groups can also be beneficial in managing the emotional impact of dental issues.
Conclusion
My journey to healing my receding gums has been a transformative experience, highlighting the importance of proactive oral care, early intervention, and a holistic approach to dental health. While the road to recovery was not always easy, the results have been incredibly rewarding.
By combining professional dental treatments, lifestyle changes, and a commitment to ongoing maintenance, I was able to reverse the progression of my gum recession and restore the health and appearance of my smile. The key takeaways from my experience include:
- Early detection and treatment: Seeking professional dental care at the first signs of gum recession can greatly improve the chances of reversing or halting the condition before it progresses further.
- Proper oral hygiene: Brushing and flossing correctly, using desensitizing toothpaste, and avoiding aggressive techniques are crucial for maintaining healthy gums.
- Lifestyle factors: Quitting smoking, managing stress levels, and maintaining a balanced diet can all contribute to better overall oral health and promote healing.
- Consistency and patience: Healing receding gums is a gradual process that requires consistent effort and patience. Sticking to the recommended treatment plan and routines is essential for achieving long-term success.
- Addressing emotional and social impacts: Receding gums can have a significant emotional and social impact, and it’s important to seek support and prioritize self-care throughout the healing journey.
I hope that by sharing my experience and the insights gained, I can inspire others who are facing similar challenges with receding gums. Remember, with the right treatment, commitment, and support, it is possible to heal and maintain healthy gums for a lifetime of confident smiles.


